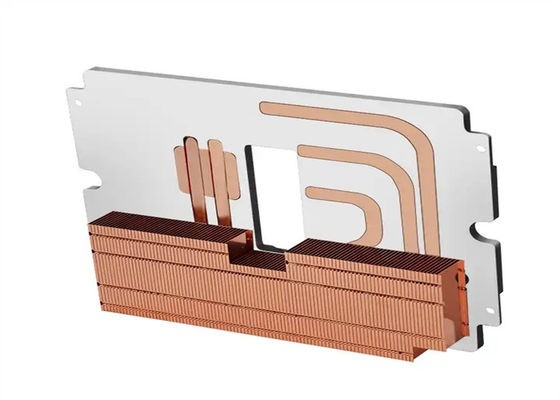
In the efficient operation of modern electronic devices, heat dissipation is of crucial importance. As a high-performance heat dissipation solution, ceramic heat sinks are gradually emerging and have been widely used in numerous fields due to their unique advantages.
I. Material Properties
Ceramic heat sinks are mainly made of high-performance ceramic materials such as alumina (Al₂O₃) and aluminum nitride (AlN). These materials have excellent properties, laying a solid foundation for the efficient operation of heat sinks. Taking alumina as an example, 96% purity alumina ceramics can have a thermal conductivity of 24 - 35W/m·K, which is more than 10 times that of traditional epoxy resins, enabling rapid conduction of heat. At the same time, its volume resistivity is >10¹⁴Ω·cm, and it can withstand a high-voltage breakdown of up to 15kV. While ensuring good thermal conductivity, it provides extremely high electrical insulation, effectively preventing the risk of short circuits. In addition, ceramic materials also have a high melting point. For instance, the melting point of alumina ceramics is as high as 2054°C, which can remain stable in high-temperature environments and ensure the continuous and normal operation of the heat sink.
II. Heat Dissipation Principle
The heat dissipation principle of ceramic heat sinks is based on their special structure and material properties. On one hand, ceramics themselves have low heat capacity and do not store heat, so heat can be quickly conducted to the outside through ceramics, reducing the accumulation of heat inside the equipment. On the other hand, some ceramic heat sinks adopt a micro-porous structure, which can have 30% more porosity under the same unit area, greatly increasing the contact area with convective media such as air, significantly enhancing the heat convection effect, and thus being able to take away more heat in the same unit time. Moreover, the polycrystalline structure of ceramics further enhances the heat dissipation capacity, surpassing most thermally conductive and insulating materials available on the market under the same conditions.
III. Performance Advantages
- Efficient Heat Dissipation: The high thermal conductivity allows ceramic heat sinks to quickly conduct heat from the heating element to the outside, effectively reducing the operating temperature of the equipment. For example, in an actual test of a 5G base station, the chip temperature dropped by 12°C after installing the ceramic heat sink, strongly ensuring the stable operation of the base station equipment.
- High Electrical Insulation: Excellent electrical insulation performance ensures that the heat sink will not cause electrical faults such as short circuits in high-voltage environments, providing reliable protection for the safe operation of electronic equipment, especially suitable for application scenarios with strict insulation requirements, such as new energy vehicle battery modules.
- High Temperature Resistance and Corrosion Resistance: It can withstand high-temperature environments and has good resistance to acids, alkalis and other chemical substances. It can still maintain stable performance in harsh working environments, greatly extending its service life. For example, in the application of photovoltaic inverters, 99% alumina ceramic heat-conducting sheets can work stably in a desert environment with a high temperature of 70°C, much sand and wind, and strong ultraviolet rays, while the traditional aluminum sheet heat dissipation scheme has a sharp increase in thermal resistance due to oxidation.
- Anti-interference and Anti-static: It can effectively resist interference (EMI) and static electricity, reduce the impact of external electromagnetic interference on the equipment, and avoid damage to electronic components caused by static electricity, improving the stability and reliability of equipment operation.
- Small Size and Light Weight: While providing efficient heat dissipation, it occupies a small space and is light in weight, conforming to the design trend of modern equipment being thin, light, short and small, and facilitating the compact layout and portable design of products.
- Environmental Protection: Ceramics are natural organic materials, which are environmentally friendly during production and use, conforming to the current environmental protection concepts and relevant environmental protection requirements.
IV. Application Fields
- Electronic Devices: Widely used in consumer electronic products such as mobile phones, laptops, and tablet computers. For example, a certain brand's flagship mobile phone embeds a 0.2mm alumina ceramic heat-conducting sheet between the CPU and the shell. After playing "Genshin Impact" for half an hour, the body temperature drops from 48°C to 36°C, and the frame rate is stable at 60fps, significantly improving the user's gaming experience. In laptops, ceramic heat sinks replace traditional thermal grease, reducing the volume of the heat dissipation module by 30%, creating conditions for thin and light laptops to be equipped with standard-voltage CPUs.
- New Energy Vehicles: It is crucial for the thermal management of batteries. Tesla's 4680 battery pack uses porous ceramic heat-conducting sheets with a thermal conductivity of 30W/m·K. Combined with the liquid cooling system, the temperature difference of the battery cells is controlled within ±2°C, effectively reducing the risk of battery thermal runaway. A domestic automaker's actual measurement shows that the probability of thermal runaway of the battery pack without ceramic sheets during fast charging is 8 times that of the one with ceramic sheets installed.
- Photovoltaic Inverters: In photovoltaic power stations, inverters generate a lot of heat during long-term operation. The inverters in Dunhuang Photovoltaic Power Station use 99% alumina ceramic heat-conducting sheets, which can still work stably in harsh environments with high temperature, strong ultraviolet rays and much sand and wind, ensuring the efficient power generation of the photovoltaic system.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: In applications such as wafer lithography equipment carriers, nano-scale alumina ceramic heat-conducting sheets can achieve a temperature control accuracy of ±0.01°C, ensuring that temperature fluctuations do not affect circuit accuracy during photoresist exposure, and improving the yield rate of chip manufacturing. According to data from a packaging factory, the chip yield rate increased by 3.2% after using ceramic heat-conducting sheets.
- Other Fields: It is also widely used in set-top boxes, LED lights, high-frequency welding machines, power amplifiers/speakers, power transistors, power modules, inverters, network/broadband, UPS power supplies and other equipment, as well as aerospace, industrial manufacturing and other fields with high requirements for heat dissipation and material performance, providing reliable heat dissipation protection for the stable operation of various equipment.
V. Customization Services
We are well aware that different customers have different needs, so we provide comprehensive customization services. Whether it is size, shape, or material selection, we can tailor-make according to your specific requirements. From common standard sizes such as TO - 220, TO - 247, TO - 264, TO - 3P to various non-standard sizes, we can produce accurately. At the same time, according to your emphasis on different performance indicators such as heat dissipation performance, electrical insulation, and temperature resistance, we can recommend and select the most suitable ceramic materials, such as alumina and aluminum nitride, and optimize the materials to meet your specific application scenarios.
With its excellent performance and wide applicability, ceramic heat sinks provide an ideal solution for solving the heat dissipation problems of modern equipment. Choosing our ceramic heat sinks means choosing efficient, safe and reliable heat dissipation protection, which can guarantee the performance improvement and stable operation of your equipment.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!